INSIDE OUR EARTH VIDEO LINK
NOTES
What is the Earth?
(i) The earth is a dynamic planet and comprises of three layers: crust, mantle and core.
(ii) Constant changes take place inside as well as outside the earth.
Interior of the Earth:
(i) The Earth is made of several concrete layers.
(ii) The uppermost layer over the earth’s surface is called the crust. It is the thinnest of all the layers. It is about 35 km on the continental masses and only 5 km on the ocean floors.
(iii) Silica (Si) and alumina (Al) are the main mineral constituents of the continental mass. It is, thus, called sial.
(iv) The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica (Si) and magnesium (Mg) called sima.
(v) Just below the crust is the mantle up to an extent of 2,900 km.
(vi) The innermost layer is core with a radius of 3,500 km. As it is made of nickel (Ni) and iron (Fe), it is called nife. The central core has very high temperature and pressure.
Rocks and Minerals:
(i) The earth’s crust is made of various types of rocks. Any natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust is called a rock.
(ii) There are three major types of rocks; igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks.
(iii) When the molten magma cools, it becomes solid. Rocks thus formed are called igneous or primary rocks. They are of two types, extrusive igneous rocks and intrusive igneous rocks.
- When molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid. Rocks formed in such a way on the crust are called extrusive igneous rocks. They have a very fine grained structure. For example, basalt.
- Sometimes, the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust. Solid rocks so formed are called intrusive igneous rocks. Since they cool down slowly, they form large grains. Granite is an example of such a rock.
(iv) Rocks roll down and break into small fragments and these smaller particles are called sediments. These sediments are transported, compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks. These types of rocks are called sedimentary rocks.
(v) Igneous and sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks under great heat and pressure. For example, clay changes into slate and limestone into marble.
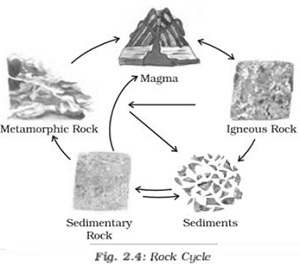
(vi) The process of transformation of the rock from one to another is called the rock cycle.
- When the molten magma cools; it solidifies to become igneous rock. Theseigneous rocks are broken down into small particles that are transported and deposited to form sedimentary rocks.
- When the igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to heat and pressure, they change into metamorphic rocks.
- The metamorphic rocks which are still under great heat and pressure melt down to form molten magma. This molten magma again can cool down and solidify intoigneous rocks.
(vii) Rocks are made of different minerals. Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition.
EXERCISE
Q1. Answer the following questions:
- What are the three layers of the earth?
- What is a rock?
- Name three types of rocks.
- How are extrusive and intrusive rocks formed?
- What do you mean by a rock cycle?
- What are the uses of rocks?
- What are metamorphic rocks?
Answers:
- The Earth is made up of several concentric layers with one inside another just like the onion. The three layers of the earth are the crust, the mantle, and the core. The uppermost layer or crust is the thinnest of all layers. It is 35 km on the continental masses and only 5 km on the ocean floors. Just beneath the crust is the mantle which extends up to a depth of 2900 km. The innermost layer is the core with a radius of about 3500 km. It is made up of nickel and iron and is therefore called a knife. The central core has very high temperature and pressure. The crust forms only 0.5 percent of the volume of the earth, 16 percent consists of the mantle and 83 percent makes the core.
- Rock or stone is a natural substance, a solid aggregate of one or more minerals or mineraloids. For example, granite, a common rock, is a combination of the minerals quartz, feldspar and biotite. The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock.
- Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks are the three types of rocks.
- Both extrusive and intrusive rocks are examples of igneous rocks. Igneous rocks are also known as primary rocks. Extrusive rocks are formed when the molten magma present inside the earth's interior comes out onto the earth's surface, cools down rapidly and becomes solid on the earth's crust. These rocks have a very fine-grained structure. For example, basalt. Deccan plateau is made of basalt rocks. When molten magma cools down and solidifies deep within the earth's crust, intrusive rocks are formed. Since they cool down slowly, they form large grains. Granite is an example of such a rock. Grinding stones used to prepare paste/powder of spices and grains are made of granite. Nowadays, granite is also used for flooring.
- The transformation of one type of rock into another, under certain conditions and in a cyclic manner is referred to as the rock cycle. For example, igneous rocks, formed as a result of the solidification of molten magma, may break down into smaller particles, which may then be transported and deposited to form sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary and igneous rocks transform into metamorphic rocks when subjected to heat and pressure. These metamorphic rocks may themselves get broken down to form sedimentary rocks, or they may melt under great heat and pressure to form molten magma, which would then once again solidify to form igneous rocks.
- Some of the uses of rocks are as follows:
- For building roads, houses, and other buildings
- The mineral gold is used for making jewellery
- For cutting and drilling purposes
- The fossil remains of plants and animals present in rocks help in scientific research.
- The different minerals that make up different rocks are used as fuels, medicines, fertilizers, and in various industries.
- Stones are used to playing many games.
- The word Metamorphic is derived from the Greek word Metamorphose which means the change of form. Metamorphic rocks are the rocks that get formed under great heat and pressure. They are formed when Igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to heat and pressure. For example, clay changes to slate and limestone into marble.
Q2. Tick the correct answer.
| (i) Core | (e) Innermost layer |
| (ii) Minerals | (d) Has definite chemical composition |
| (iii) Rocks | (b) Used for roads and buildings |
| (iv) Clay | (a) Changes into slate |
| (v) Sial | (c) Made of silicon and alumina |

| Object | Minerals most commonly used in them |
| Karhai | Iron, copper, stainless steel,teflon |
| Ornaments | Gold, silver, platinum |
| Lamp | Brass, silver, gold, copper |
| Hammer | Iron, steel, lead, brass |
| Bell | Brass, silver, gold |
| Pan/tava | Iron, steel, aluminium,teflon |
(ii) Pencil lead is made of graphite. Telephones have copper wiring. Carpets in our homes contain sulphur and chromite. Clocks are made of Quartz and Pentlandite. Toothpaste is made white with titanium oxide which comes from minerals called rutile, ilmenite and anatase.